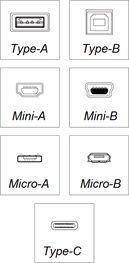
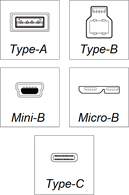
About USB

Type-A and Type-B connectors
- Use with SMART products
Connecting to touch from computer inputs
Connecting USB drives and other peripherals

Type-C connectors
- Use with SMART products
Connecting to video, audio, and touch from computer inputs
Connecting and providing power to USB peripherals
Universal Serial Bus (USB) is a standard for data exchange and data power between electronic devices, such as SMART Board interactive displays.
Cable selection checklist
Summary | Details | |
|---|---|---|
The cable is of high quality. | Poor quality USB cables that do not meet industry standards can cause issues with a SMART product’s touch functions or connected USB peripherals. Poor quality cables can also cause unexpected behavior with SMART’s software products (such as SMART Notebook collaborative learning software) when the software is used with a SMART product or other touch-enabled display. | |
The cable is certified. | Look for cables that have the USB certification logo. The logo indicates the cable has passed the USB Implementations Forum (USB-IF) regulatory body’s compliance testing for product quality. | |
The cable supports the required speed. |
About USB cable versions
These are the main versions of USB cable available:
Version | Speed | Maximum cable length | Connector types |
|---|---|---|---|
USB 2.0 Low Speed 1 | 1.5 Mbps |
| |
USB 2.0 Full Speed 2 | 12 Mbps |
| |
USB 2.0 High Speed | 480 Mbps |
| |
USB 3.2 Gen 1 SuperSpeed 3 | 5 Gbps |
| |
USB 3.2 Gen 2 SuperSpeedPlus 4 | 10 Gbps |
| |
USB 3.2 Gen 2×2 Enhanced SuperSpeed | 20 Gbps |
| |
USB4 | 40 Gbps |
|
The main differences among versions are the available power delivery and data transfer speeds. Cables that support newer versions (USB 3.2 and USB4) carry more power and have faster data-transfer speeds. USB 3.2 is backwards compatible with USB 2.0. USB4 technology is backward compatible with USB 3.2 and 2.0 devices, as well as Thunderbolt 3 and 4. Although SMART products support all versions, cables that support USB 2.0 Hi-Speed or newer are recommended.
Note
Although USB 3.2 and USB4 are designed to be backwards compatible, the compatibility can be less than 100%. For example, you might experience issues when using USB 3.2 with USB 2.0. If you experience issues while using a USB 3.2 connection, try connecting a USB 2.0 hub between the SMART product and the computer. If the issues persist, use a USB 2.0 cable instead of a USB 3.2 one or contact the computer’s manufacturer. To guarantee the best USB performance, make sure the latest USB 3.2 chipset drivers are installed on the computer.
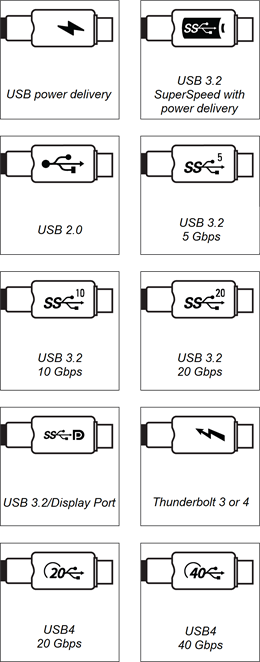
Differentiating USB Type-C cables
USB Type-C connectors serve different purposes. For this reason, not all USB Type-C cables are the same. For example:
Some USB Type-C cables provide power only.
Some USB Type-C cables support USB 2.0 data only.
Some USB Type-C cables support SuperSpeed USB data and/or video data.
Refer to a cable’s packaging, if available, to determine its features and capabilities.
In addition, you can refer to symbols that might appear on the cable.
If a symbol doesn’t appear on the cable, you might need to test the capable to determine its capabilities.
SMART recommends using USB Type-C cables that support at least USB 3.2 Gen 1 SuperSpeed data when connecting to USB Type-C connectors on SMART Board interactive displays.
USB Type-C cable symbols
Extending USB cables
Improperly extended USB connections can cause a SMART product’s touch features to behave unexpectedly.
SMART offers two options for extending USB connections:
Active USB extension cable (USB‑XT) for USB 2.0 Hi-Speed
CAT 5 USB extender (CAT5-XT-1100) for USB 2.0 Full-Speed
USB tier structure
The USB bus has a tiered star topology with a hub at the center of each star. The maximum number of tiers allowed is seven, so the maximum number of hubs between a host and a device allowed is five.
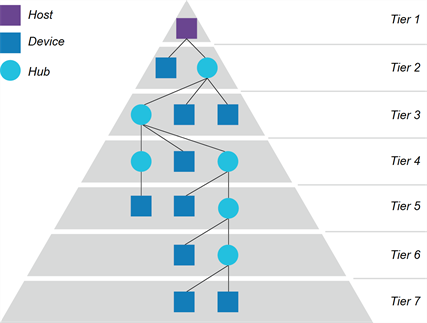
Keep this in mind when extending a USB connection between a host and device. Also, when counting the number of hubs between a host and device, be aware that newer SMART Board interactive displays include internal USB hubs.
An improperly extended USB connection is likely to work only intermittently or not at all. For most SMART products, check if the indicator light is not solid green to tell if an issue is USB related or SMART Product Drivers software isn’t running correctly.
Selecting USB cable extenders
SMART provides support only for its own USB cable extenders and recommends using these extenders because they have been designed and tested to work with SMART products. However, if this isn’t possible, use products from well-established, reputable companies.
Use only active USB cable extenders. Active extenders help maintain the signal strength as the data is transmitted across longer distances.
SMART cannot provide support for USB extension beyond the supplied USB cable or the use of non-SMART USB cable extenders.
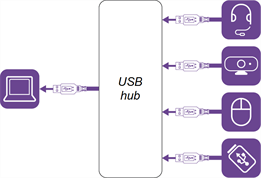
Using USB hubs
A common scenario in which you might need a USB hub is when you have only one USB receptacle available on a computer but need to connect multiple devices, such as a headset, a camera, a mouse, and a USB drive. Hubs also let you consolidate USB-connected devices into one receptacle, making it possible to disable all the devices at once by disconnecting a single cable.
Note
Newer SMART Board interactive displays include internal USB hubs, allowing you to connect USB peripherals to a computer through the display.
USB hub types
- Bus-powered
A bus-powered hub draws its power from the USB source device, such as a computer. A bus-powered hub doesn’t need a separate power connection. It can’t provide more power to the downstream devices than that provided by the USB source device. If you use a bus-powered hub with an extension cable, you can quickly run out of power. You should purchase a USB hub with a separate power adapter.
- Self-powered
A self-powered hub draws power from an external power supply and provides up to 500 mA for USB 2.0, up to 900 mA for USB 3.2, and more for USB 3.2 and USB4 with USB PD (Power Delivery) support to power each of the connected USB devices. The amount of power depends on the specifications of the hub, cable, and connected device.
- Dynamic-powered
A dynamic powered hub is a combination of bus-powered and self-powered hub. It automatically switches between modes if a separate power supply is available.