About power cables and connectors

- Use with SMART products
Connecting to a power source
Power cables can be grounded (three-pronged) or ungrounded (two-pronged). Grounded power cables limit the buildup of static electricity, reducing the chances of electric shock and damage to audio systems and other sensitive equipment.
SMART products feature a standard International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) interface and provide certified, country-specific power cables. SMART recommends that you always use the power cable provided with the SMART product because the cable has been appropriately sized for the SMART product.
Cable selection checklist
Summary | Details | |
|---|---|---|
The cable meets country-specific power requirements. | Power standards vary among regions, and you’ll need to use a power cable that supports your region’s voltages and frequencies. Although you can use adapters to make power cables compatible with local power sources, first verify that the adapter and the device being connected can handle the necessary voltage conversion. | |
The cable is appropriate for the load current. | Device power cables can be rated for use with different load currents. Make sure the power cable is rated to safely handle more current than a connected device will draw. See the specifications for the SMART product for power consumption information. If only a power rating is provided, the current can be calculated using the following formula: 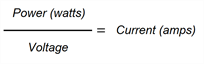 | |
The SMART Board interactive display and any connected computers are connected to the same power outlet or bar. | In many schools and offices, two adjacent power outlets can be on different power phases. If you connect the display to one outlet and the computer to another on a different power phase, you might hear a whine or buzzing sound. |
About RS-232

- Use with SMART products
Send commands from a computer
Connecting multiple SMART Board interactive displays
RS-232 is a standard for the serial communication of data between data terminal equipment (DTE), such as a computer, and data communication equipment (DCE), such as a computer modem, a room control system, or a control port on electronic equipment. When using an RS‑232 connection, be sure to test it with a terminal program on a computer first.
The RS-232 standard defines the electrical characteristics, timing and meaning of signals, and the physical size and pinout of connectors. The standard doesn’t define the data commands and responses, which are device specific. Although RS-232 connectors were once common on computers and peripheral devices, such as printers and modems, they have been phased out in most modern devices in favor of USB connectors.
RS-232 serial cables are used to connect an RS-232 connector on the DTE device to an RS-232 connector on the DCE device.
Most modern computers don’t include an RS-232 connector, so if you need to connect a computer and a SMART product using an RS-232 serial cable, you’ll need an external USB to RS-232 converter.
Cable selection checklist
Summary | Details | |
|---|---|---|
The cable isn’t a “null” modem cable. | Unless they are specifically required, null modem cables should not be used except when troubleshooting connections. Null modem cables can be identified by the word “null” stamped on them. Null modem cables are also characterized with a crossover of the transmitter and receiver pins. |
About Ethernet (network)

- Use with SMART products
Connecting to networks
Ethernet is a type of Local Area Network (LAN) technology. Ethernet differs from a Wireless Local Area Network (WLAN) in that it requires physical twisted-pair network cables to connect devices, such as a computer and a network router. Different varieties of network cable exist, the most common of which are currently Cat 5e (Category 5 enhanced), Cat 6 (Category 6), and Cat 7 (Category 7). Network cables can be shielded to protect against electromagnetic interference (EMI) which can interfere with communication through the network cable.
Cable selection checklist
Summary | |
|---|---|
The cable is rated for the data communications speed and category of the network and connected equipment (for example, Cat 5e, Cat 6, or Cat 7). |
